Unified Multimodal 64-Bit Arithmetic Logic Unit for High-Performance Computing Architectures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31838/JCVS/07.02.01Keywords:
Unified ALU; Parallel processing; Floating-point arithmetic; Fixed-point arithmetic; Machine learning hardware; Cryptographic computationsAbstract
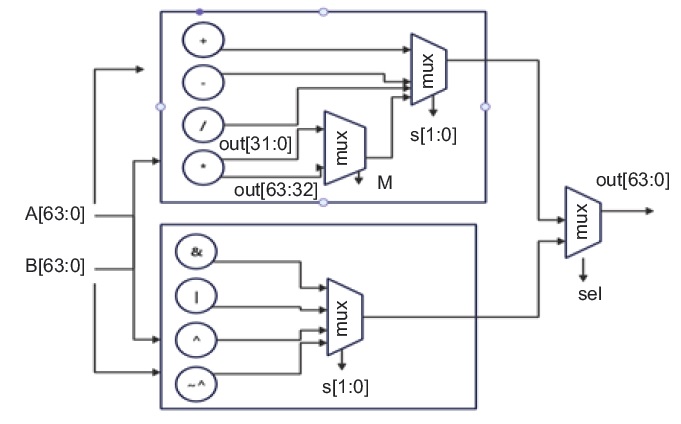
An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the core component for any processing unit to perform arithmetical and logical operations for modern computing. The design for ALUs for specific tasks including integer and floating-point arithmetic, logical operations, data movement, and control functions influences the CPU architecture and digital system design. This work presents a unified ALU implemented in Verilog hardware description language (HDL), capable of performing arithmetic and logic operations across diverse numerical representations. The ALU is engineered to integrate logic unit, signed arithmetic processor, unsigned arithmetic processor, and floating-point arithmetic processor. The selection of operation is governed by select line signals to facilitate versatile user-driven functionality at the hardware level. To enhance the computational efficiency for handling multiplication of 64-bit signed and unsigned operands which generates 128-bit result, the proposed ALU architecture employs parallelism by processing the most significant and least significant bits simultaneously. A flexible mechanism for selective output enables the user to extract the desired segment of the result. Consolidating floating-point and fixed-point computations within a single ALU instance, the proposed architecture reduces the silicon area with reduced power dissipation and computational latency while streamlining routing complexities. This multi-modal ALU design with high-throughput is particularly suited for deployment in heterogeneous computing environments such as general-purpose processors, cryptographic accelerators, and machine intelligence hardware, where the rapid processing of heterogeneous data types is essential for workload optimization and energy-efficient system operation.