Quantum-Inspired VLSI Architectures for Secure Cryptographic Signal Processing in Next-Generation AI-enabled hardware systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31838/JCVS/07.02.10Keywords:
Quantum-Inspired VLSI, Secure Cryptographic Hardware, AI Accelerators, Signal Processing, Reversible Logic, Low-Power ArchitecturesAbstract
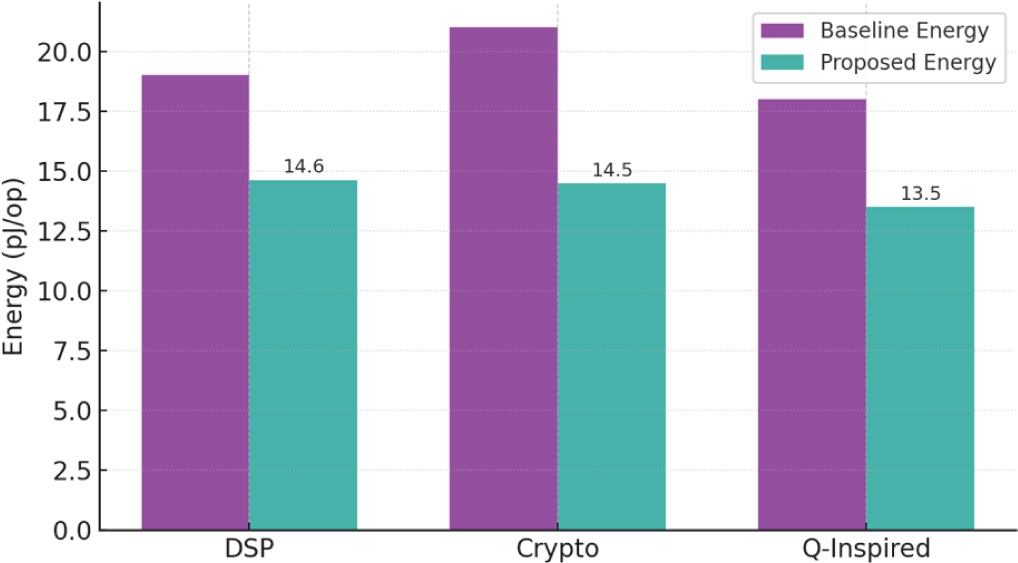
The sudden advent of AI-driven platforms and smart cyber-physical systems have rendered more and more demands on hardware frameworks that are capable of delivering quantum-inspired processing, secure cryptographic processing, and efficient signal-processing aptitudes all at once. The conventional VLSI architectures are constrained by the deterministic logic models which do not reflect the probabilistic characteristic of the quantum-inspired algorithms and the advanced cryptographic models. In order to fill this gap, this work introduces a single quantum-inspired VLSI that is optimised to implement secure signal processing in AI hardware of the next generation. The suggested system will combine approximate probabilistic computing blocks, reversible-logic embedded datapaths, and lightweight quantum-state emulation units to aid in increasing security, decreasing power usage, supporting parallel cryptographic transformations. The optimization methods based on machine learning are applied to explore architectures, allowing reconfiguration of cryptographic workloads and neural inference workloads and signal-processing workloads dynamically. The use of 5 nm and 7 nm technology nodes leads to simulation studies which show great improvement in throughput-per-watt, encryption latency and resistance to side-channel vulnerabilities. The architecture also minimises signal-processing overhead and signification of cryptographic diffusion properties which are important to edge AI deployments. The given work provides an addition of a scaleable quantum-inspired design model that can bridge the gap between traditional VLSI and new post-quantum computing requirements, and provide secure, energy-efficient, AI-operated hardware systems that can support defense, autonomous infrastructures, and future Internet of Things.