Machine Learning-Assisted Automated VLSI Design for Bioinformatics Hardware Accelerators with Embedded Cryptographic Security
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31838/JCVS/07.02.04Keywords:
Automated VLSI design, Bioinformatics accelerators, Machine learning, Cryptographic hardware security, Reinforcement learning, Hardware–software co-design, Secure biomedical computingAbstract
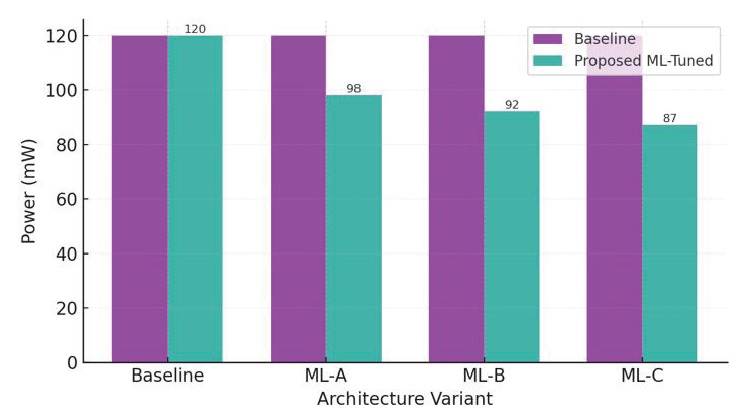
The growing need of high-throughput bioinformatics computation, and the strict data privacy demands has further triggered the need to have hardware accelerators with both sophisticated processing and in-built cryptographic protection. The given paper introduces a machine learning-aided automated VLSI design system that should be used to create next-generation bioinformatics accelerators with embedded security primitives. The suggested approach capitalizes on the design-space exploration based on the learning approach, adaptive hardware synthesis, and on-board encryption to facilitate genomic alignment, protein structure modelling, and multi-omics signal analysis. Reinforcement learning and trained prediction models are auto-generate architectural choices which can be used to optimize datapaths, memory subsystems, and cryptographic blocks. Lightweight AES, hash and PUF authentication units embedded are used to guarantee confidentiality and integrity in biomedical processes where compliance with regulation is paramount. The given framework would be beneficial to both the edge and cloud-connected biomedical system because it allows increasing design scalability and decreasing the amount of manual engineering overhead. The experimental tests show that it is more efficient in design, has less power consumption, and is more efficient in computational throughput than traditional VLSI techniques. This is further enhanced by the fact that the ML-directed optimization further minimises development cycles, and guarantees security-performance balance of various bioinformatics kernels. This work introduces a single design paradigm, which is a unification of automated VLSI synthesis, machine intelligence, and cryptographic protection of secure biomedical hardware acceleration.