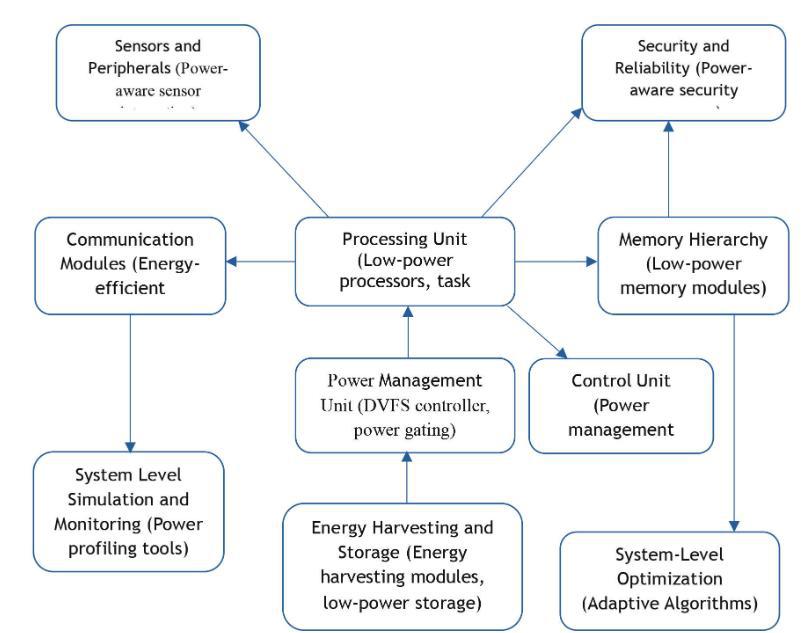
Adaptive VLSI Design Using Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) for Low-Latency IoT Communication Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31838/jvcs/07.01.03Keywords:
Adaptive VLSI, Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS), IoT Communication Networks, Low-Latency, Power-Efficient Design, Real-Time Systems, Energy Optimization, Hardware Acceleration.Abstract
The best and most compatible hardware solutions need to be developed to meet the growing demand for communication in Internet of Things (IoT) networks. This paper suggests using dynamic voltage and frequency scaling or DVFS for designing adaptive VLSI circuits for small IoT communication networks. DVFS is used to adjust the operating voltage and frequency of circuits and reduce power consumption when network traffic is light. It also maintains high-speed operation under heavy loads. By satisfying the requirements of the oscillating network the proposed VLSI design preserves low latency and high power efficiency. Simulations and prototype implementations show that in comparison to conventional VLSI designs the system features notable improvements in both communication speed and power consumption. These findings show that by strengthening power and traffic performance in IoT networks through the integration of VLSI circuits DVFS can be a good option for resource-constrained IoT devices and real-time applications.